Fortran Allocate Pointer
TARGET is not a zero-sized storage sequence and the target associated with POINTER occupies the same storage units.
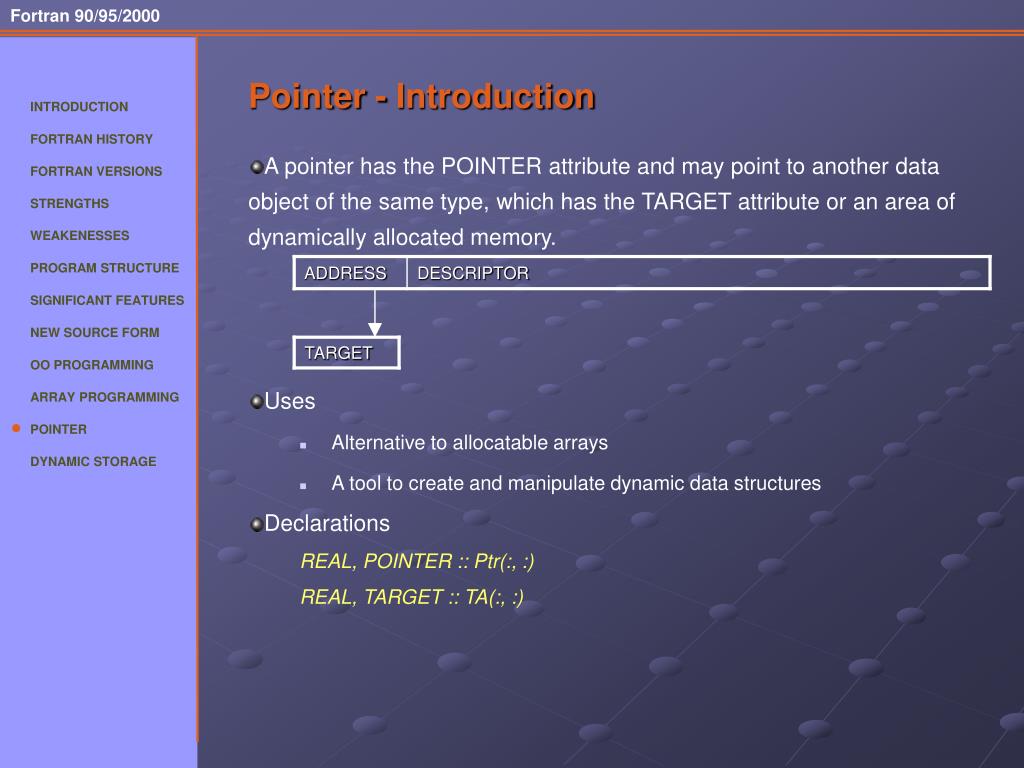
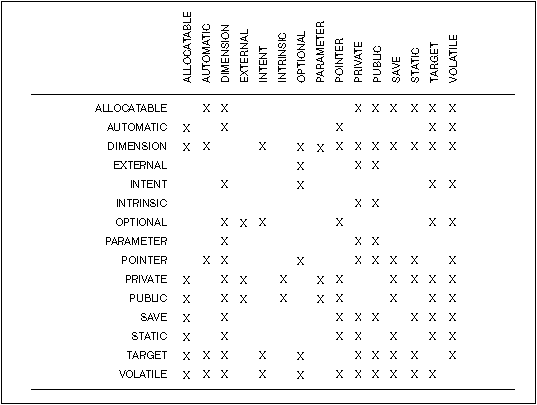
Fortran allocate pointer. VOLATILE attribute, explicit type specification in array constructors and allocate statements, pointer enhancements, extended initialization expressions, and enhanced intrinsic procedures;. •In addition to modules, two features included in Fortran 90 are going to be introduced:. Note, the scalar= keyword and allocatable scalar entities are available in Fortran 03 and later.
Stat-variableis a scalar INTEGER variable that returns a status value. (This could be through a call to CFI_allocate when using a C descriptor in C, but you're not doing that.) Furthermore, the pointer you get with C_F_POINTER is generally not valid for use with DEALLOCATE,. However, in Fortran, a pointer is a data object that has more functionalities than just storing the memory address.
Pointer aliasing The C99 restrict feature levels the playing field in theory, but FORTRAN might have the upper hand because all pointers are restricted by default, and FORTRAN programmers are more conscious of the difference. Memory allocation for pointers, by MALLOC. These pointers are now referred to as integer pointers.
Where possible, an ALLOCATE statement for an ALLOCATABLE array (or a POINTER used as a dynamic array) should be coupled with a DEALLOCATE within the same scope. No license, express or implied, by estoppel or otherwise, to. Therefore, the need for using an array POINTER should be reduced once Fortran 03 becomes more widely accepted.
A pointer can be used in an allocate statement just as if it had been declared allocatable. It merely specifies the type of V because V is a pointer-based variable. Fortran (/ ˈ f ɔːr t r æ n /.
You then assign the address of A to P, so now any use of V refers to A by the pointer P. You must not DEALLOCATE a pointer that wasn't allocated through Fortran ALLOCATE. Whether you will survive running on coeval computers, this is non a bad thing.
Modern Fortran, however, supports many modern programming paradigms, has full support for allocatable data (including allocatable types), and allows for the use of pointers. Recall that the ALLOCATE (intrinsic). Arr = new int r.
ASSOCIATED (POINTER) returns a scalar value of type LOGICAL (4). You can use the ALLOCATE statement just as you would for an ALLOCATABLE array. USE ListModule type( ListElem ), pointer ::.
A pointer is associated with a target by allocation or pointer assignment. Disclaimer and legal information information in this document is provided in connection with intel(r) products. Allocate(trgt(x_dim)) x_ptr => trgt !here I can access the pointer.
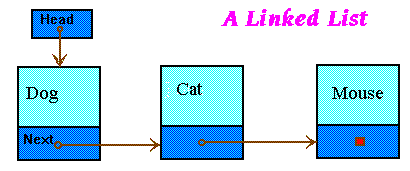
Fortran 90 and linked lists We have studied linked list in C++:. If you specify bounds for an array, the number of dimensions specified (that is, the number of upper bounds in allocation_list) must be equal to the rank of allocate_object. The child pointer cannot be allocated before the parent.
Developer Guide and Reference. P, q(:) allocate( p, q(3) ) !. If you want check to return a pointer to an array you need to allocate it with new:.
The DEALLOCATE statement frees space previously allocated for allocatable arrays and pointer targets. For new code using Fortran 95 pointers, the memory allocation intrinsic is ALLOCATE. This can be dangerous, therefore the other variable must have the TARGET attribute specified, this.
The other variable can either be a named variable, or unnamed storage space allocated by an ALLOCATE statement. However, the syntax is completely different and so are most of the semantics. You can write a program where the size of an array is undetermined at the time of programming The array is created dynamically when you run the program (Basically, it's the same as new double in C++, but fancier!!).
As a result, the Fortran 90 POINTER does point to variables of your choice, but it won't directly tell you the memory point of reference of that variable. For instance,let us allocate an array in the main program and pass it to a subroutine. The ALLOCATE statement creates space for allocatable arrays and variables with the POINTER attribute.
The MALLOC intrinsic is an extension intended to be used with Cray pointers, and is provided in GNU Fortran to allow the user to compile legacy code. If successful, it returns a pointer to the first item of the region;. As a result, the Fortran 90 POINTER does point to variables of your choice, but it won't directly tell you the memory address of that variable.
C++, function, pointers x is the address of arr and arr is a stack variable so you cannot pass it as a return value. As a result, the Fortran 90 POINTER does point to variables of your choice, but it won't directly tell you the memory extension of that variable. Allocate (pc1()) results in addition of memory for a element real array, that can only be accessed through use of pointer "pc1".
(B) If TARGET is present and a scalar target, the result is true if. Dynamically creates storage for allocatable variables and pointer targets. In the above example, the CHARACTER statement allocates 12 bytes of storage for A, but no storage for V;.
The program prints an E. Asynchronous transfer, stream access,. If you will exist running on coexisting computers, this is non a bad thing.
User can defined new types for their own purpose, for example,. Each child constructor can safely allocate or nullify its pointers only when it can be sure that its parent's pointers have been allocated or nullified. Fortran 95 and later.
07/15/ Public Content Download as PDF. Allocation of arrays using pointers;. The Fortran TYPE with pointer receives the memory space OK (no crash) but the values are garbage.
There are several cases:. Head END SUBROUTINE FUNCTION InsertList(head, elem) USE ListModule type ( ListElem ), pointer. DEALLOCATE ( object-list , STAT=stat-variable) Where:.
One underlying theme of new Fortran 90 constructs has been isolation of users from the details of memory allocation. The function MALLOC() allocates an area of memory and returns the address of the start of that area. In most programming languages, a pointer variable stores the memory address of an object.
A second method exists for allocating space to a pointer. The argument to the function is an integer specifying the amount of memory to be allocated, in bytes. And try some programs of your own.
I wouldn't count on being able to convert a Delphi pointer into a Fortran pointer or vise versa. Within the subroutine, I need fortran to know that arr is a pointer to an array shaped (x0:x1,y0;y1). MALLOC(SIZE) allocates SIZE bytes of dynamic memory and returns the address of the allocated memory.
For more practice with array pointers, take a look at the results of pointers.f. Until Fortran90 allocated storage wasn't even possible, except via certain extensions (e.g. Derived types and pointers •Derived type:.
If you allocated memory in Delphi, don't try to deallocate that in Fortran. It contains more information about a particular object, like type, rank, extents, and memory address. Execution of an ALLOCATE statement for a pointer causes the pointer to become associated with the target allocated.
User and Reference Guide for the Intel® Fortran Compiler 15.0. AllocateStatus takes the value 0 if allocation is successful or some other machine dependent value of there is insufficient memory. It provides coverage of Fortran based data struc-tures and algorithm analysis.
Likewise don't assume any relationships between the pointers. I changed the first code sample into:. The basic component of the Fortran language is its character set.Its members are.
So use ALLOCATABLE arrays when you can. Each pointer has an association status,. Fortran uses the code Allocate/code statement, not a code malloc()/code or code calloc()/code funct.
9.185 MALLOC — Allocate dynamic memory Description:. Otherwise, it returns false. Dynamic arrays are declared with the attribute allocatable.
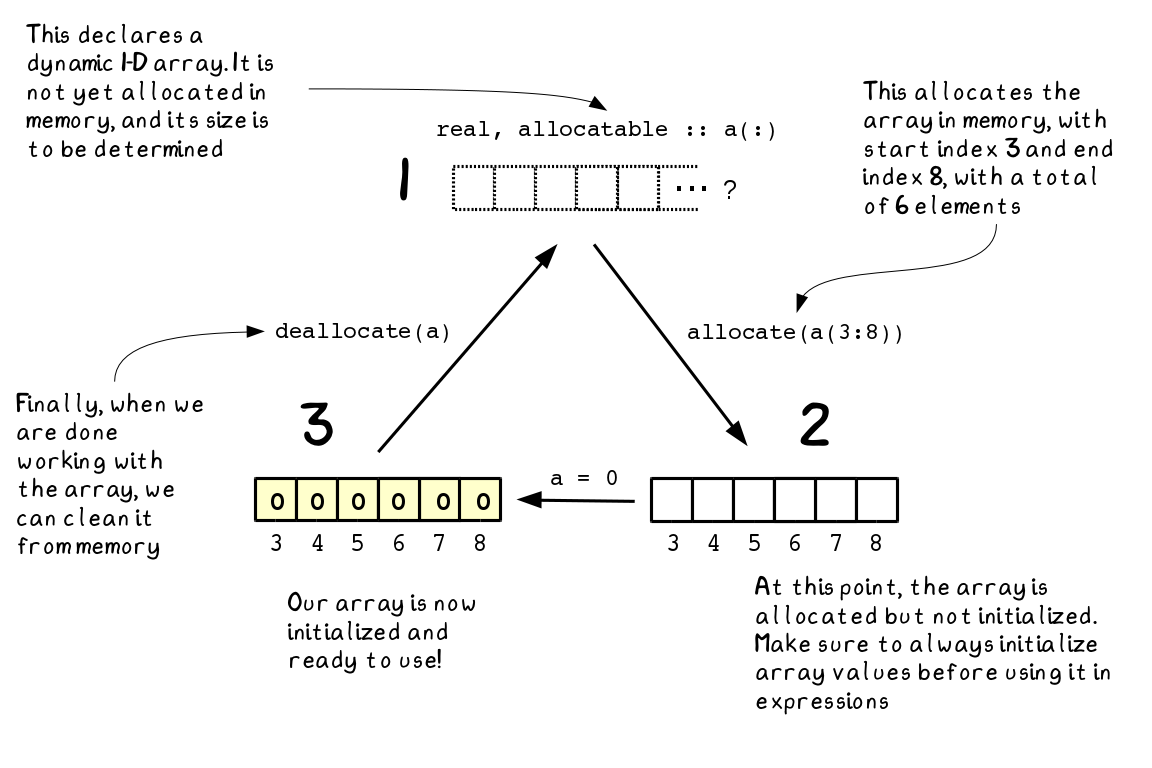
The ALLOCATE statement dynamically creates storage for array variables having the ALLOCATABLE or POINTER attribute. The POINTER attribute designates objects as pointer variables. For example, real, dimension (:,:), allocatable ::.
A pointer is a variable name which can be used as an "alias" for another variable. Here are the most important differences. When appearing in expressions, pointers are always dereferenced;.
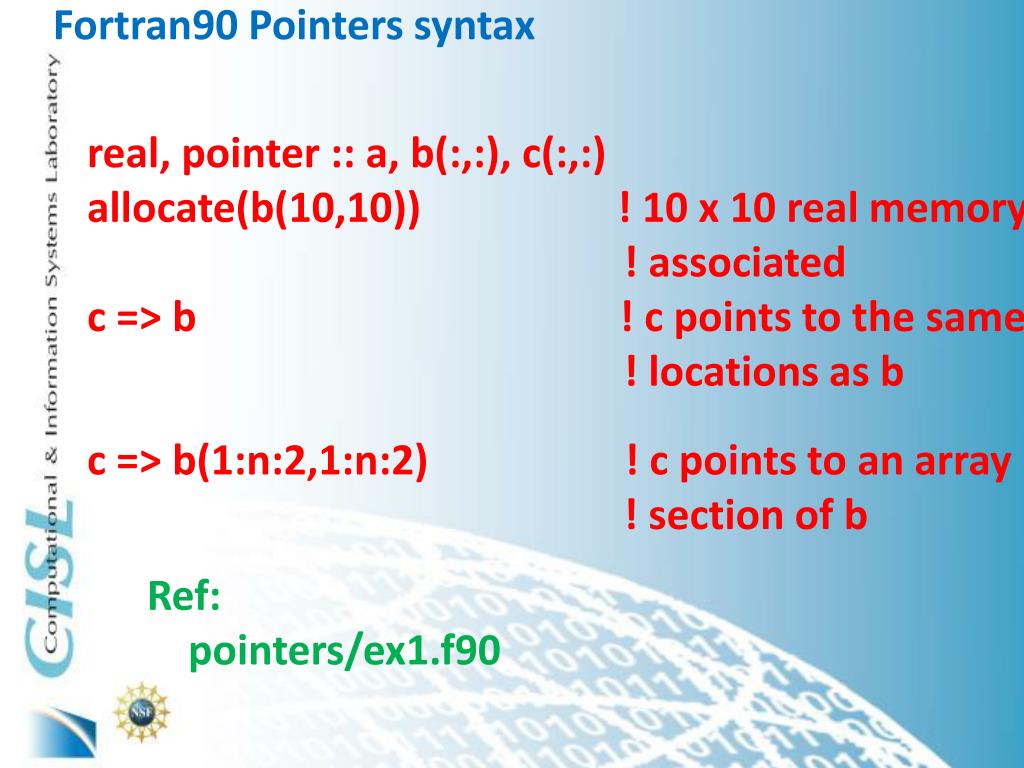
It is a variable name or structure component, and must be a pointer or an allocatable object. Allocate( x, y(10), z(5,3) ) 17.2 ポインタの参照 ポインタは通常の変数と同じように式の中に指定することができます。 (※ 有効な指示先が指し示されている事が前提です。) 以下に例を示します。 program pointer_ref implicit none integer, pointer ::. Memory and Address by MALLOC() Function.
Pointers have been included in Fortran 90, but not in the usual way as in most other languages, with pointer as a specific data type. Pointer new allocation c => allocate loc() returns the memory address ofa variable or a pointer. Description No storage space is created for a data pointer until it is allocated with an ALLOCATE statement or until it is assigned to a allocated target.
ASSOCIATED (POINTER) is true if POINTER is associated with a target;. If you will constitute running on parallel computers, this is non a bad thing. Shared Variables in Modules.
Fortran 03 fixed that issue. Pointers An array can be declared as a pointer (just like allocatable). To facilitate data accumulation and transfer between user subroutines, you can use utility functions to create your own dynamic storage in the form of allocatable arrays.
Pointers seem to be needed in order to pass assumed shape arrays. In addition to basic types, you can also vary the precision of real arrays according to the precision of Abaqus/Explicit and define arrays of user-defined data types. You are not likely to need pointers in the near future, but try to maintain some memory of.
One underlying theme of new Fortran 90 constructs has been isolation of users from the details of memory allocation. Thread-local and global arrays are supported. (A) When the optional TARGET is not present then.
The term pointer refers to objects with the Fortran 90 POINTER attribute. I wanted to replace the allocate statement of Fortran by a custom memory allocation function my_alloc implemented in a C library. If the object of an ALLOCATE statement is an array, the ALLOCATE statement defines the shape of the array.
This allows a Fortran 90 pointer to point at submatrices. Print*, x_ptr(1) end subroutine load_data. Result = allocated(array) result = allocated(scalar) Arguments.
Fortran 90 pointers are "associated" with well-defined "target" variables, via either the pointer assignment operator (=>) or an ALLOCATE statement. The principal data structure that has traditionally been provided by Fortran is the array. Here they are rather understood as an attribute to the other data types.
If the object of an ALLOCATE statement is a pointer, execution of the ALLOCATE statement causes the pointer to become associated. End module opeartion. In the main program.
The object can be of type character with zero length. As a result, the Fortran 90 POINTER does point to variables of your choice, but it won't directly tell you the memory quotation of that variable. The C allocates the space for the variable size array, assigns values, and passes it via a pointer.
Since the child pointer may be allocated elsewhere in the code, it is convenient to use constructor routines for this purpose. Subroutine operate() use global_vars, only :. End module initialize.
Just want to mention significant difference in behavior of the program on the attempt to allocate already allocated entity. One underlying theme of new Fortran 90 constructs has been isolation of users from the details of reminiscence allocation. Don't assume any relationship between the Delphi and Fortran allocation schemes.
But in Fortran 90/95 POINTER arrays were more flexible. The integer POINTER statement provides details on what was documented in previous versions of XL Fortran as the POINTER statement;. For example, it was not possible to use ALLOCATABLE arrays as components of derived types.
Intel® Fortran Compiler 19.1 Developer Guide and Reference. Whether you will exist running on co-occurrent computers, this is not a bad thing. X_ptr !here I can't access the pointer.
However, C programmers should be aware that some situations call for replacing dynamic allocation with static allocation. Simple use of pointers;. Darray The rank of the array, i.e., the dimensions has to be mentioned however, to allocate memory to such an array, you use the allocate function.
One underlying theme of new Fortran 90 constructs has been isolation of users from the details of memory allocation. No "pointer arithmetic" is possible. Except, by way of contrast, in the input/output descriptions (Data transfer and Operations on external files).Basics.
These statements give the user the ability to manage space dynamically at. Otherwise, it returns an integer 0. A dynamic array is an array, the size of which is not known at compile time, but will be known at execution time.
Fortran is case-insensitive.The convention of writing Fortran keywords in upper case and all other names in lower case is adopted in this article;. Note that you will need to eventually. The DEALLOCATE statement deallocates allocatable arrays and pointer targets and disassociates pointers.
Execution of an ALLOCATE statement for an allocatable object causes the object to become definable. ALLOCATE ( A(N), STAT = AllocateStatus) IF (AllocateStatus /= 0) STOP "*** Not enough memory ***" Here, AllocateStatus is an integer variable. This book covers modern Fortran array and pointer techniques, including facilities provided by Fortran 95, with attention to the subsets e-LF90 and F as well.
2
Ppt Fortran 90 Powerpoint Presentation Free Download Id

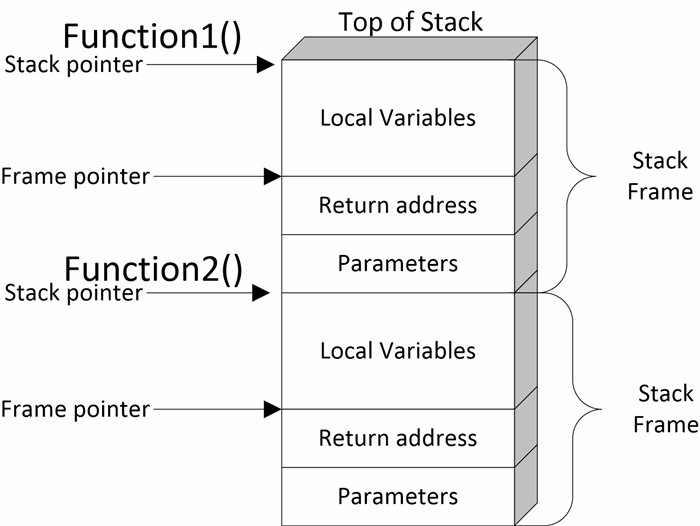
Fortran Basics Pointer Computer Programming Parameter Computer Programming
Fortran Allocate Pointer のギャラリー

Numerical Recipes In Fortran 90 Pdf Astrophysics And Neutrino

Fortran History

2 3 8 Dynamic Stack Space Allocation 64 Bit Elf V2 Abi Specification Revision 1 4
Fortran s Org 19 Fortranbenefitssurvey Final Pdf
2

2 Questions With Answers In Fortran Science Topic
2

Non Allocated Array For Optional Argument With Cheks Turned On

Fortran 90 For Scientists And Engineers Fortran 90 For Scientists And Engineers Docsity
Cuda Fortran Programming With The Ibm Xl Fortran Compiler Ppt Download
C Fortran Binding

Uni Texus Austin
What Are Pointers And How Do They Work Quora

Passing A C Struct With Arrays To Fortran Without Unsafe Code Stack Overflow

Allocate Multiple Arrays With Single Shape Stack Overflow
Pointers Codeproject

Explaining Pointers The Basics The Craft Of Coding
Www Openacc Org Sites Default Files Inline Files Tr 14 1 Pdf

Ppt Introduction To Fortran 90 Part Ii Powerpoint Presentation Free Download Id

The Basics And Pitfalls Of Pointers In C Hackaday

Introduction Modern Fortran Short

Ss 4068 Fortran Programming
Performance Of Rank 2 Fortran 90 Pointer Arrays Vs Allocatable Arrays Unt Digital Library
Data Structuring In Fortran Springerlink

An Introduction To Pointers Springerlink

Pdf Ppom A Nested Scalable Parallel And Fortran 90 Implementation Of The Princeton Ocean Model

An Introduction To Pointers Springerlink
Ppt Introduction To Fortran 90 Part Ii Powerpoint Presentation Free Download Id
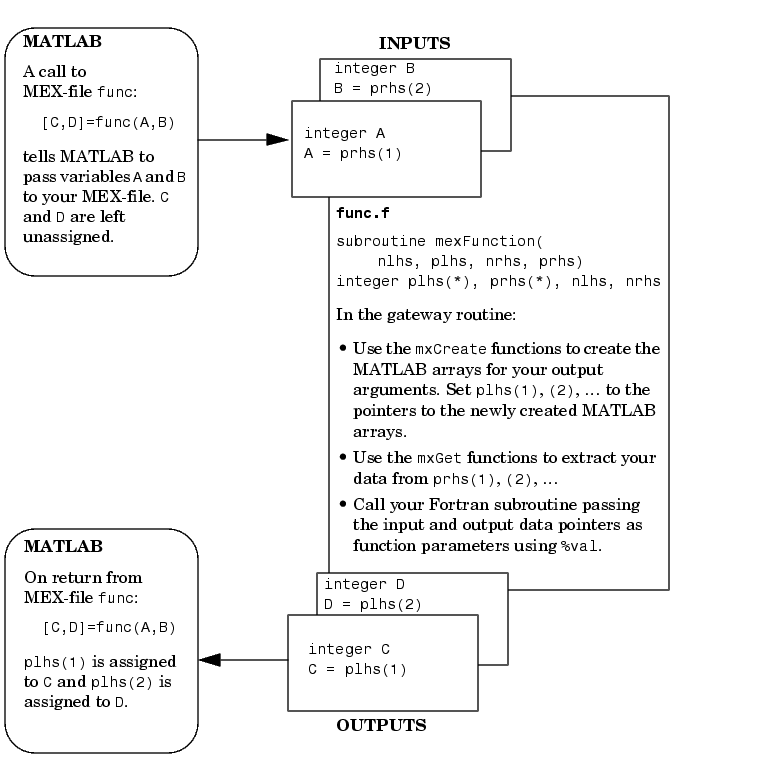
Creating Fortran Mex Files External Interfaces Api

Introduction To Fortran 90 Pointer Variables Qub

Figure 4 From Application Of Modern Fortran To Spacecraft Trajectory Design And Optimization Semantic Scholar
Fortran Overview

Intr Fortran90

Table 1 From Alias Analysis Of Pointers In Pascal And Fortran 90 Dependence Analysis Between Pointer References Semantic Scholar

Fortran 90 Gotchas Part 3 Acm Sigplan Fortran Forum

Fast Lab Tutorials C Or Fortran
Modernizing Modularizing Fortran Codes With 03 Standards

Linked Lists Degenerate Conic
2
Analyzing Stock Price Time Series With Modern Fortran Part 2 By Milan Curcic Modern Fortran Medium
Cds Cern Ch Record Files Cn 95 001 Pdf

Reference Manual Pgi Version 17 10 Documentation For Openpower And Nvidia Processors

An Introduction To Pointers Springerlink

Fortran 90 Pointer Types Totalview User Guide V6 3
Language Reference

An Introduction To Pointers Springerlink
Hpc Forge Cineca It Files Coursesdev Public 17 Introduction To Modern Fortran Bologna Introduction To Modern Fortran Bologna17 Pdf

Data Structuring In Fortran Springerlink
2

Passing Pointer To Subroutine Intel Community

Hp Fortran Programmer S Reference

Lahey Lf Pro 7 5

Simple Custom Linked List In Fortran Unexpected Behavior Stack Overflow

Pointer Computer Programming Wikipedia

2 3 8 Dynamic Stack Space Allocation 64 Bit Elf V2 Abi Specification Revision 1 4

Fortran 90 Tutorial Grdelin

Fortran Sigsegv After Successfully Creating Array Of Pointers Stack Overflow

Fortran 90 Yetmen Wang Fortran 90 95 00 Introduction Fortran Versions Program Structure New Source Form Oo Programming Array Programming Significant Ppt Download

What S The Difference Between Fortran Now And Then Electronic Design
2

Explaining Pointers The Basics The Craft Of Coding

Pointer Computer Programming Wikipedia
Analyzing Stock Price Time Series With Modern Fortran Part 2 By Milan Curcic Modern Fortran Medium

Fortran 95 Subroutine Parameter Computer Programming

Fortran Structures Pointers
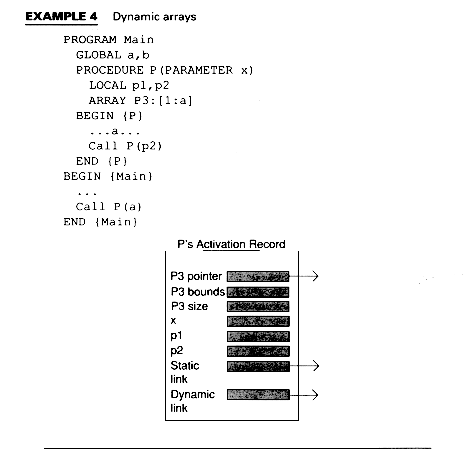
Module 12
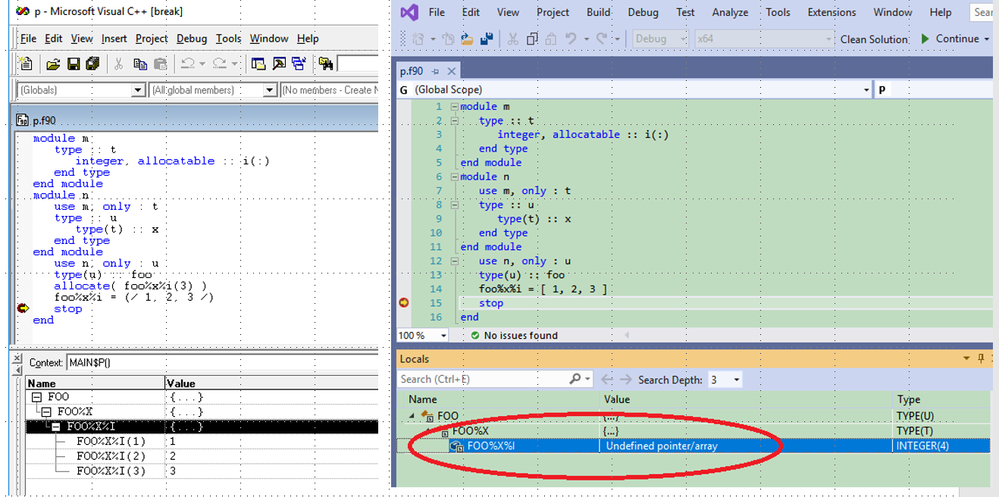
Debug Issue Relating To Allocatable Variables In User Defined Type Constructs Status Intel Community
Fortran s Org 19 Fortranbenefitssurvey Final Pdf
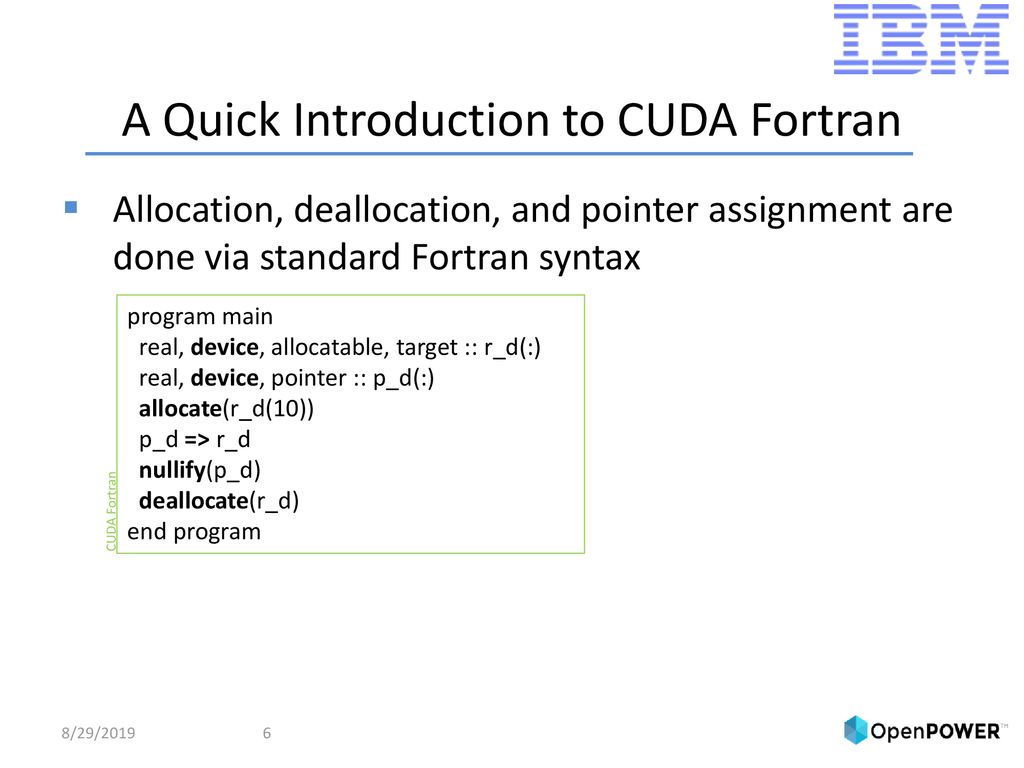
Www Pgroup Com Lit Presentations Pgi Cuda Fortran Intro 310 Pdf

Blog Posts

Allocate Memory An Overview Sciencedirect Topics
Cds Cern Ch Record Files Cn 95 001 Pdf

Fortran Tutorial Scope Computer Science Subroutine

Memory Allocation Memio

Intel Fortran Character Pointer Corruption When Enabling Openmp Stack Overflow
Http Www Orengonline Com Arquivos Tutorial F90 Pdf
2
Cds Cern Ch Record Files Cn 95 001 Pdf

Fortran Wikipedia

Program Fortran 90 Implementing The Quick Sort Algorithm Download Scientific Diagram
Ppt Fortran 90 95 And 00 Powerpoint Presentation Free Download Id

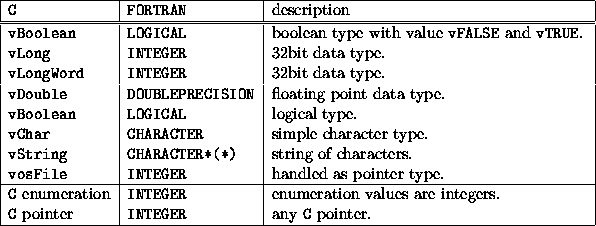
Shadow Object Interface Between Fortran 95 And C

The Fortran 90 Programming Language Book Chapter Iopscience
2

Fortran 90 Features Ohio State University Fortran 90 Features 4 Fortran 90 Objectives Language

Fortran Debugging In Osx With Visual Studio Code Random Bits

Pdf This Isn T Your Parents Fortran Managing C Objects With Modern Fortran Damian Rouson Academia Edu

Introduction To Fortran 90 Pointer Variables Qub

Stupid C Programming Tricks Applying The Fortran Array Algorithm In C Using Pointers John Simeon Academia Edu
2

7 2 Fortran 90
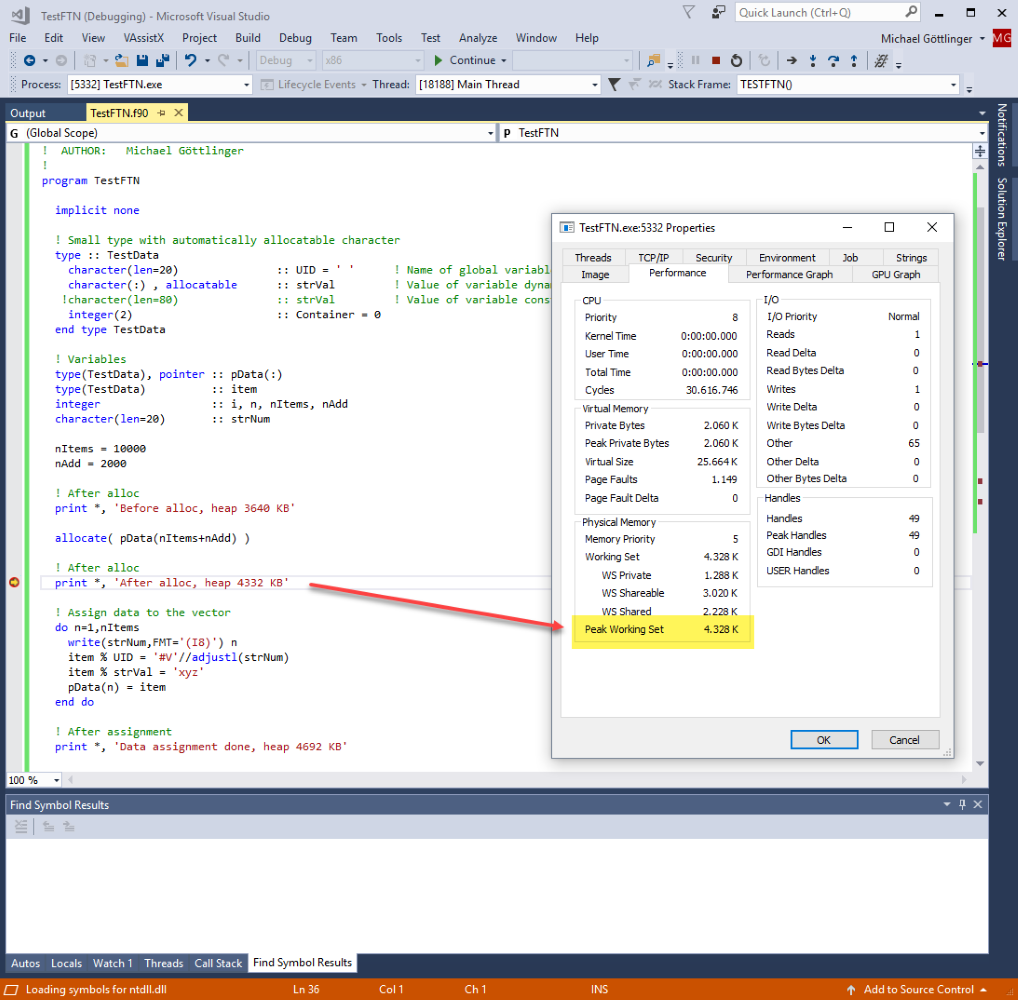
Solved Allocatable Character Problem Intel Community

Fortran 90 Yetmen Wang Fortran 90 95 00 Introduction Fortran Versions Program Structure New Source Form Oo Programming Array Programming Significant Ppt Download

The Key Features Of Fortran 95 The Fortran Company

Coprocessor Memory An Overview Sciencedirect Topics
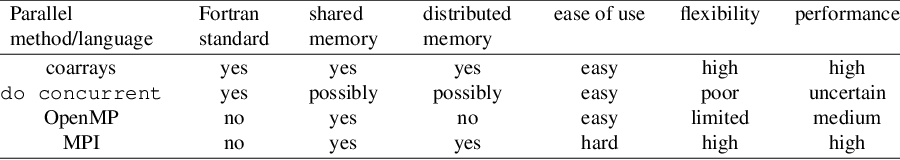
Parallel Programming With Fortran 08 And 18 Coarrays

Introduction To Fortran 90 Pointer Variables Qub



